Understanding the Pipeline Configuration
🔄 Understanding the CI/CD Pipeline Configuration
Now that we’ve set up the GitHub connection and deployed our CloudFormation template, let’s understand how our CI/CD pipeline is configured to integrate Docker Build Cloud, Docker Scout, and Amazon ECS deployment.
📋 Pipeline Architecture Overview
Our CloudFormation template creates a complete CI/CD pipeline with these key components:
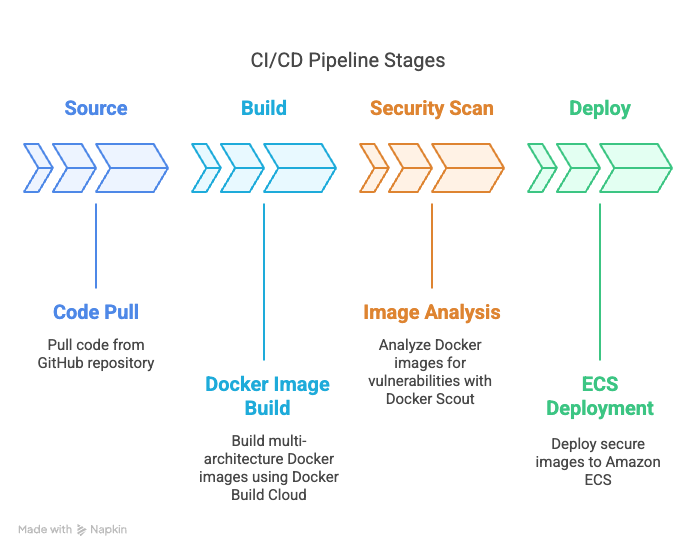
- Source Stage: Pulls code from your GitHub repository
- Build Stage: Uses Docker Build Cloud for efficient container image building
- Security Scan Stage: Integrates Docker Scout for vulnerability assessment
- Deploy Stage: Deploys the application to Amazon ECS
🔍 Key Components in the CloudFormation Template
Let’s examine the key components in our CloudFormation template that power our pipeline:
1️⃣ Docker Build Cloud Integration
The template includes a CodeBuild project specifically configured to use Docker Build Cloud:
# CodeBuild Project for Docker Build
DockerBuildProject:
Type: AWS::CodeBuild::Project
Properties:
Name: docker-build-cloud-project
Description: "Build Docker image using Docker Build Cloud and push to Docker Hub"
ServiceRole: !GetAtt CodeBuildServiceRole.Arn
Artifacts:
Type: CODEPIPELINE
Environment:
Type: ARM_CONTAINER
ComputeType: BUILD_GENERAL1_SMALL
Image: aws/codebuild/amazonlinux2-aarch64-standard:2.0
PrivilegedMode: true
Source:
Type: CODEPIPELINE
BuildSpec: |
version: 0.2
env:
secrets-manager:
DOCKER_USERNAME: "dockerhub-credentials:DOCKER_USERNAME"
DOCKER_TOKEN: "dockerhub-credentials:DOCKER_TOKEN"
phases:
pre_build:
commands:
- echo Logging in to Docker Hub...
- echo $DOCKER_TOKEN | docker login -u $DOCKER_USERNAME --password-stdin
- echo Setting up Docker Buildx...
- docker version
- mkdir -p ~/.docker/cli-plugins/
- curl -SL https://github.com/docker/buildx/releases/download/v0.10.4/buildx-v0.10.4.linux-arm64 -o ~/.docker/cli-plugins/docker-buildx
- chmod +x ~/.docker/cli-plugins/docker-buildx
- docker buildx version
- docker buildx create --name mybuilder --driver docker-container
- docker buildx use mybuilder
- docker buildx inspect --bootstrap
- COMMIT_HASH=$(echo $CODEBUILD_RESOLVED_SOURCE_VERSION | cut -c 1-7)
- IMAGE_TAG=${COMMIT_HASH:=latest}
build:
commands:
- echo Building Docker image using BuildKit...
- docker buildx build --platform linux/arm64 -t $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:latest -t $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG --push .
post_build:
commands:
- echo Docker image pushed to Docker Hub
- echo Writing image definitions file...
- echo '[{"name":"rent-a-room","imageUri":"'$DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG'"}]' > imagedefinitions.json
artifacts:
files:
- imagedefinitions.json
🔹 Key Elements of the Docker Build Configuration
| Element | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_CONTAINER | Uses ARM-based build environment | Optimized for building ARM64 images |
| PrivilegedMode: true | Enables Docker-in-Docker capabilities | Required for Docker Buildx |
| docker buildx | Sets up Docker’s multi-architecture build tool | Enables advanced build features |
| –platform linux/arm64 | Specifies target architecture | Ensures compatibility with ARM-based ECS instances |
| –push | Pushes directly to registry | Streamlines the build and push process |
🔹 Multi-Architecture Build Capabilities
While our current pipeline is configured specifically for ARM64 to match our ECS task definition, Docker Build Cloud supports multi-architecture builds. With a simple modification, you could build for multiple architectures simultaneously:
# Example of multi-architecture build command
docker buildx build --platform linux/amd64,linux/arm64 -t $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:latest --push .
This capability allows you to:
- Build once, deploy anywhere
- Support both x86 (AMD64) and ARM-based (ARM64) environments
- Optimize for AWS Graviton processors while maintaining compatibility with traditional instances
- Automatically serve the right image architecture to different environments
2️⃣ Docker Scout Security Integration
The template includes a dedicated CodeBuild project for Docker Scout security scanning:
# CodeBuild Project for Docker Scout Security Scan
DockerScoutProject:
Type: AWS::CodeBuild::Project
Properties:
Name: docker-scout-scan-project
Description: 'Scan Docker image using Docker Scout'
ServiceRole: !GetAtt CodeBuildServiceRole.Arn
Artifacts:
Type: CODEPIPELINE
Environment:
Type: ARM_CONTAINER
ComputeType: BUILD_GENERAL1_SMALL
Image: aws/codebuild/amazonlinux2-aarch64-standard:2.0
PrivilegedMode: true
Source:
Type: CODEPIPELINE
BuildSpec: |
version: 0.2
env:
secrets-manager:
DOCKER_USERNAME: "dockerhub-credentials:DOCKER_USERNAME"
DOCKER_TOKEN: "dockerhub-credentials:DOCKER_TOKEN"
phases:
pre_build:
commands:
- echo Logging in to Docker Hub...
- echo $DOCKER_TOKEN | docker login -u $DOCKER_USERNAME --password-stdin
- COMMIT_HASH=$(echo $CODEBUILD_RESOLVED_SOURCE_VERSION | cut -c 1-7)
- IMAGE_TAG=${COMMIT_HASH:=latest}
build:
commands:
- echo Running Docker Scout security scan...
- docker pull $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG
# Run Docker Scout with security gates
- >
docker run --rm
-e DOCKER_SCOUT_HUB_USER=$DOCKER_USERNAME
-e DOCKER_SCOUT_HUB_PASSWORD=$DOCKER_TOKEN
docker/scout-cli cves $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG --exit-code --only-severity critical,high
- echo "No critical or high vulnerabilities found. Scan passed!"
- >
docker run --rm
-e DOCKER_SCOUT_HUB_USER=$DOCKER_USERNAME
-e DOCKER_SCOUT_HUB_PASSWORD=$DOCKER_TOKEN
docker/scout-cli recommendations $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG
post_build:
commands:
- echo Security scan completed
- echo Generating security report...
- >
docker run --rm
-e DOCKER_SCOUT_HUB_USER=$DOCKER_USERNAME
-e DOCKER_SCOUT_HUB_PASSWORD=$DOCKER_TOKEN
docker/scout-cli cves $DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG --format json > security-report.json
- echo "Creating imagedefinitions.json file"
- echo '[{"name":"rent-a-room","imageUri":"'$DOCKER_USERNAME/rent-a-room:$IMAGE_TAG'"}]' > imagedefinitions.json
artifacts:
files:
- security-report.json
- imagedefinitions.json
🔹 Key Elements of the Docker Scout Integration
| Element | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| docker/scout-cli | Uses Docker Scout CLI in a container | No need to install Scout separately |
| –exit-code –only-severity critical,high | Implements security gates | Fails the build if critical/high vulnerabilities are found |
| recommendations | Generates improvement suggestions | Provides actionable security insights |
| –format json > security-report.json | Creates structured security report | Enables automated analysis and reporting |
3️⃣ Complete Pipeline Structure
The CloudFormation template defines a complete pipeline that connects all these components:
# CodePipeline
Pipeline:
Type: AWS::CodePipeline::Pipeline
Properties:
RoleArn: !GetAtt CodePipelineServiceRole.Arn
ArtifactStore:
Type: S3
Location: !Ref ArtifactBucket
Stages:
# Source Stage - Pull from GitHub
- Name: Source
Actions:
- Name: Source
ActionTypeId:
Category: Source
Owner: AWS
Provider: CodeStarSourceConnection
Version: "1"
Configuration:
ConnectionArn: !Ref CodeStarConnectionArn
FullRepositoryId: !Sub ${GitHubOwner}/${GitHubRepo}
BranchName: !Ref GitHubBranch
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: SourceCode
# Build Stage - Build Docker image with Docker Build Cloud
- Name: Build
Actions:
- Name: BuildDockerImage
ActionTypeId:
Category: Build
Owner: AWS
Provider: CodeBuild
Version: "1"
Configuration:
ProjectName: !Ref DockerBuildProject
InputArtifacts:
- Name: SourceCode
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: BuildOutput
# Security Scan Stage - Scan with Docker Scout
- Name: SecurityScan
Actions:
- Name: DockerScoutScan
ActionTypeId:
Category: Build
Owner: AWS
Provider: CodeBuild
Version: "1"
Configuration:
ProjectName: !Ref DockerScoutProject
InputArtifacts:
- Name: BuildOutput
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: SecurityScanOutput
# Deploy Stage - Deploy to ECS
- Name: Deploy
Actions:
- Name: DeployToECS
ActionTypeId:
Category: Deploy
Owner: AWS
Provider: ECS
Version: "1"
Configuration:
ClusterName: !Ref ECSClusterName
ServiceName: !Ref ECSServiceName
FileName: imagedefinitions.json
InputArtifacts:
- Name: SecurityScanOutput
🔹 Pipeline Stages Explained
| Stage | Purpose | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Pull code from GitHub | CodeStar Connection, GitHub repository |
| Build | Build Docker image | Docker Build Cloud, Buildx, ARM64 optimization |
| Security Scan | Scan for vulnerabilities | Docker Scout, Security gates, Recommendations |
| Deploy | Deploy to ECS | Amazon ECS, Container deployment |
💡 How Docker Technologies Integrate
The pipeline seamlessly integrates Docker technologies:
-
Docker Build Cloud with Buildx:
- Optimizes build performance with distributed building
- Supports ARM64 architecture for AWS Graviton compatibility
- Streamlines the build and push process
-
Docker Scout:
- Implements security gates to prevent vulnerable images from being deployed
- Provides actionable recommendations for improving security
- Generates detailed security reports for compliance and auditing
-
Docker Hub:
- Securely stores container images
- Provides version control through image tagging
- Enables seamless deployment to Amazon ECS
🔍 Multi-Architecture Support
While our current pipeline is optimized specifically for ARM64 to match our ECS task definition, Docker Build Cloud’s multi-architecture capabilities are worth highlighting:
Why Multi-Architecture Matters
- AWS Graviton Support: AWS offers ARM-based Graviton processors that provide better price-performance ratio
- Flexibility: Your application can run on any ECS instance type without compatibility issues
- Future-Proofing: As cloud providers continue to diversify CPU architectures, your containers remain compatible
Enabling Multi-Architecture Builds
To enable multi-architecture builds in your own projects, you would modify the build command to:
docker buildx build --platform linux/amd64,linux/arm64 -t yourusername/yourapp:latest --push .
This creates a multi-architecture manifest that automatically serves the right image architecture based on the runtime environment.
🚀 Next Steps
Now that you understand how the pipeline is configured, let’s complete the workshop by:
- Making a change to the application
- Triggering the pipeline
- Observing the build, security scan, and deployment process
In the next section, we’ll make a personalized change to the application and watch our complete CI/CD pipeline in action!